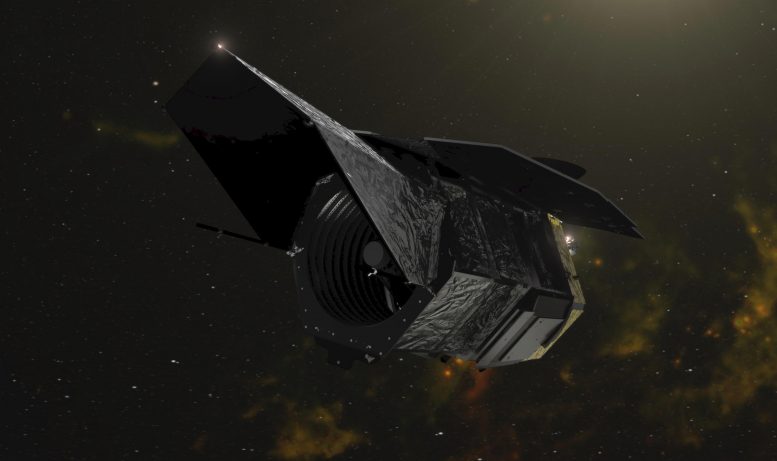
Large-resolution illustration of the Roman spacecraft versus a starry history. Credit score: NASA’s Goddard Room Flight Middle
New simulations clearly show that NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope will be ready to reveal myriad rogue planets – freely floating bodies that drift through our galaxy untethered to a star. Researching these island worlds will assist us fully grasp additional about how planetary systems form, evolve, and crack apart.
Astronomers uncovered planets beyond our solar procedure, recognized as exoplanets, in the 1990s. We quickly went from understanding of only our possess planetary process to acknowledging that planets most likely outnumber the hundreds of billions of stars in our galaxy. Now, a crew of scientists is obtaining strategies to boost our being familiar with of planet demographics by hunting for rogue worlds.
“As our watch of the universe has expanded, we have recognized that our photo voltaic system may perhaps be abnormal,” claimed Samson Johnson, a graduate college student at Ohio Condition College in Columbus who led the exploration work. “Roman will aid us discover much more about how we healthy in the cosmic scheme of matters by researching rogue planets.”
The findings, released in the Astronomical Journal, centre on the Roman Space Telescope’s capability to find and characterize isolated planets. Astronomers have only tentatively learned a handful of of these nomad worlds so much for the reason that they are so tricky to detect.
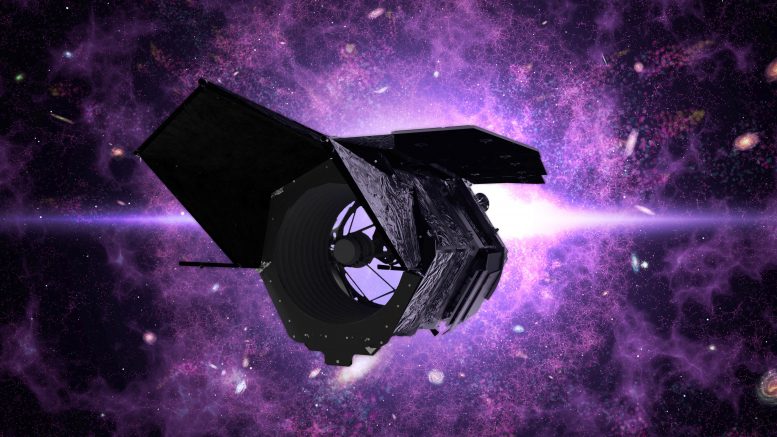

NASA’s Extensive Area Infrared Survey Telescope (WFIRST) is now named the Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope, immediately after NASA’s to start with Chief of Astronomy. Credit history: NASA
Obtaining galactic nomads
Roman will find rogue planets by conducting a substantial microlensing survey. Gravitational lensing is an observational effect that occurs for the reason that the presence of mass warps the fabric of house-time. The impact is excessive close to extremely large objects, like black holes and overall galaxies. Even solitary planets result in a detectable diploma of warping, known as microlensing.
This animation reveals how gravitational microlensing can reveal island worlds. When an unseen rogue earth passes in entrance of a a lot more distant star from our vantage position, light-weight from the star bends as it passes through the warped area-time all over the world. The planet functions as a cosmic magnifying glass, amplifying the brightness of the qualifications star. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Room Flight Center/CI Lab
If a rogue planet aligns closely with a far more distant star from our vantage position, the star’s light will bend as it travels as a result of the curved area-time about the planet. The end result is that the earth functions like a pure magnifying glass, amplifying gentle from the qualifications star. Astronomers see the influence as a spike in the star’s brightness as the star and planet appear into alignment. Measuring how the spike improvements around time reveals clues to the rogue planet’s mass.
“The microlensing sign from a rogue planet only lasts concerning a handful of several hours and a few of times and then is long gone eternally,” reported co-author Matthew Penny, an assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Louisiana Condition University in Baton Rouge. “This tends to make them difficult to observe from Earth, even with multiple telescopes. Roman is a recreation-changer for rogue world lookups.”
Microlensing gives the very best way to systematically research for rogue planets – specially these with low masses. They really don’t glow like stars and are normally very awesome objects, emitting way too very little heat for infrared telescopes to see. These vagabond worlds are effectively invisible, but Roman will explore them indirectly thanks to their gravitational effects on the light-weight of much more distant stars.
Lessons from cosmic castaways
Johnson and co-authors showed that Roman will be in a position to detect rogue planets with masses as compact as Mars. Researching these planets will support slender down competing products of planetary formation.
The planet-constructing approach can be chaotic, since smaller sized objects collide with a person a further and sometimes adhere alongside one another to type greater bodies. It is identical to using a piece of playdough to choose up other parts. But from time to time collisions and shut encounters can be so violent that they fling a planet out of the gravitational grip of its parent star. Unless it manages to drag a moon alongside with it, the freshly orphaned planet is doomed to wander the galaxy by itself.
https://www.youtube.com/check out?v=4k5nUNzmNg4
This illustration reveals a rogue planet drifting via the galaxy by itself. Credit rating: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Damage (Caltech-IPAC)
Rogue planets may perhaps also form in isolation from clouds of gas and dust, comparable to how stars develop. A modest cloud of gasoline and dust could collapse to type a central world as an alternative of a star, with moons rather of planets surrounding it.
Roman will examination planetary development and evolution styles that predict different figures of these isolated worlds. Identifying the abundance and masses of rogue planets will provide perception into the physics that drives their development. The analysis team found that the mission will present a rogue world depend that is at the very least 10 periods far more specific than existing estimates, which variety from tens of billions to trillions in our galaxy. These estimates generally arrive from observations by ground-based telescopes.
Since Roman will observe over the environment, just about a million miles absent from Earth in the direction opposite the Solar, it will produce far remarkable microlensing success. In addition to giving a sharper perspective, Roman’s standpoint will allow for it to stare at the identical patch of sky continuously for months at a time. Johnson and his colleagues confirmed that Roman’s microlensing survey will detect hundreds of rogue planets, even even though it will search only a rather narrow strip of the galaxy.
Element of the examine involved identifying how to examine the mission’s long term details to get hold of a additional exact census. Researchers will be equipped to extrapolate from Roman’s rogue earth depend to estimate how popular these objects are during the entire galaxy.
“The universe could be teeming with rogue planets and we wouldn’t even know it,” reported Scott Gaudi, a professor of astronomy at Ohio State University and a co-author of the paper. “We would never ever discover out without undertaking a complete, house-based microlensing survey like Roman is likely to do.”
For extra on this study, study Rogue Planets Could Outnumber the Stars.
Reference: “Predictions of the Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope Galactic Exoplanet Survey. II. Free-floating World Detection Rates” by Samson A. Johnson, Matthew Penny, B. Scott Gaudi, Eamonn Kerins, Nicholas J. Rattenbury, Annie C. Robin, Sebastiano Calchi Novati and Calen B. Henderson, 21 August 2020, Astronomical Journal.
DOI: 10.3847/1538-3881/aba75b
The Nancy Grace Roman Room Telescope is managed at Goddard, with participation by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Caltech/IPAC in Pasadena, the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, and a science workforce comprising scientists from analysis institutions across the United States.

Analyst. Amateur problem solver. Wannabe internet expert. Coffee geek. Tv guru. Award-winning communicator. Food nerd.