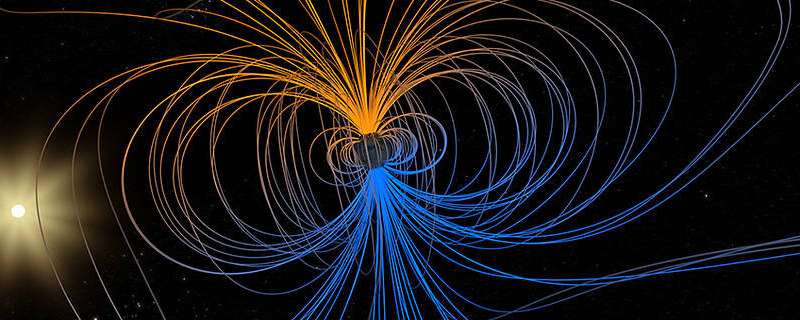
A little but evolving dent in Earth’s magnetic industry can trigger large problems for satellites.
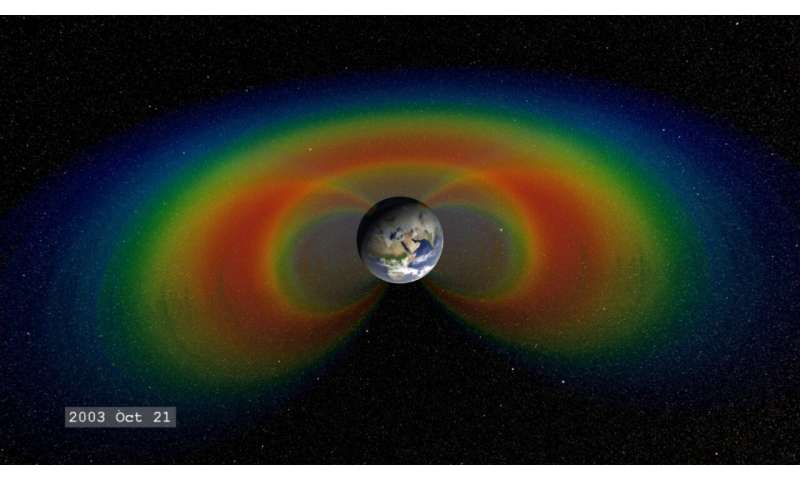
Earth’s magnetic area functions like a protecting defend about the earth, repelling and trapping charged particles from the Solar. But around South The us and the southern Atlantic Ocean, an unusually weak place in the field—called the South Atlantic Anomaly, or SAA—allows these particles to dip nearer to the surface than usual. Particle radiation in this location can knock out onboard computers and interfere with the info collection of satellites that go by way of it—a vital reason why NASA scientists want to track and study the anomaly.
The South Atlantic Anomaly is also of curiosity to NASA’s Earth researchers who keep an eye on the improvements in magnetic field toughness there, both of those for how these changes have an effect on Earth’s atmosphere and as an indicator of what is going on to Earth’s magnetic fields, deep inside of the world.
Now, the SAA generates no visible impacts on every day daily life on the floor. Even so, current observations and forecasts display that the area is expanding westward and continuing to weaken in intensity. It is also splitting—recent info shows the anomaly’s valley, or location of bare minimum field energy, has break up into two lobes, building supplemental issues for satellite missions.
A host of NASA researchers in geomagnetic, geophysics, and heliophysics study teams observe and product the SAA, to keep an eye on and forecast long run changes—and enable prepare for long run difficulties to satellites and people in place.
It truly is what is actually inside of that counts
The South Atlantic Anomaly arises from two capabilities of Earth’s core: The tilt of its magnetic axis, and the circulation of molten metals inside its outer core.
Earth is a little bit like a bar magnet, with north and south poles that depict opposing magnetic polarities and invisible magnetic industry traces encircling the world concerning them. But as opposed to a bar magnet, the main magnetic subject is not properly aligned through the world, nor is it correctly stable. That is for the reason that the subject originates from Earth’s outer main: molten, iron-rich and in vigorous movement 1800 miles down below the surface area. These churning metals act like a large generator, called the geodynamo, making electric currents that develop the magnetic subject.
https://www.youtube.com/look at?v=qpdQcw_52iM
As the main motion adjustments above time, thanks to sophisticated geodynamic ailments within the main and at the boundary with the solid mantle up earlier mentioned, the magnetic discipline fluctuates in room and time as well. These dynamical procedures in the main ripple outward to the magnetic industry encompassing the earth, building the SAA and other options in the around-Earth environment—including the tilt and drift of the magnetic poles, which are transferring around time. These evolutions in the area, which come about on a related time scale to the convection of metals in the outer core, offer experts with new clues to help them unravel the main dynamics that push the geodynamo.
“The magnetic industry is actually a superposition of fields from many latest sources,” reported Terry Sabaka, a geophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Place Flight Heart in Greenbelt, Maryland. Locations outside of the solid Earth also lead to the observed magnetic industry. Even so, he mentioned, the bulk of the industry will come from the core.
The forces in the core and the tilt of the magnetic axis jointly produce the anomaly, the spot of weaker magnetism—allowing charged particles trapped in Earth’s magnetic field to dip closer to the area.
The Sun expels a regular outflow of particles and magnetic fields acknowledged as the solar wind and extensive clouds of very hot plasma and radiation called coronal mass ejections. When this photo voltaic content streams across place and strikes Earth’s magnetosphere, the area occupied by Earth’s magnetic subject, it can turn out to be trapped and held in two donut-formed belts all over the earth termed the Van Allen Belts. The belts restrain the particles to travel along Earth’s magnetic industry strains, frequently bouncing again and forth from pole to pole. The innermost belt commences about 400 miles from the surface area of Earth, which keeps its particle radiation a nutritious length from Earth and its orbiting satellites.
However, when a notably robust storm of particles from the Sun reaches Earth, the Van Allen belts can become hugely energized and the magnetic area can be deformed, making it possible for the charged particles to penetrate the ambiance.
“The noticed SAA can be also interpreted as a consequence of weakening dominance of the dipole field in the location,” explained Weijia Kuang, a geophysicist and mathematician in Goddard’s Geodesy and Geophysics Laboratory. “Much more precisely, a localized industry with reversed polarity grows strongly in the SAA location, so generating the area depth quite weak, weaker than that of the surrounding areas.”
A pothole in space
Even though the South Atlantic Anomaly occurs from processes inside of Earth, it has results that achieve far outside of Earth’s surface area. The location can be harmful for lower-Earth orbit satellites that travel by it. If a satellite is hit by a large-electricity proton, it can brief-circuit and cause an celebration referred to as one function upset or SEU. This can induce the satellite’s perform to glitch quickly or can result in permanent injury if a key ingredient is strike. In buy to stay away from getting rid of instruments or an full satellite, operators frequently shut down non-critical parts as they pass as a result of the SAA. Indeed, NASA’s Ionospheric Link Explorer consistently travels via the area and so the mission retains frequent tabs on the SAA’s posture.

The International Area Station, which is in reduced-Earth orbit, also passes by the SAA. It is well guarded, and astronauts are safe from hurt though within. However, the ISS has other passengers affected by the greater radiation ranges: Instruments like the World wide Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation mission, or GEDI, acquire facts from numerous positions on the exterior of the ISS. The SAA brings about “blips” on GEDI’s detectors and resets the instrument’s electricity boards about the moment a month, said Bryan Blair, the mission’s deputy principal investigator and instrument scientist, and a lidar instrument scientist at Goddard.
“These functions result in no damage to GEDI,” Blair claimed. “The detector blips are uncommon in contrast to the number of laser shots—about a person blip in a million shots—and the reset line party results in a few of several hours of shed information, but it only takes place just about every month or so.”
In addition to measuring the SAA’s magnetic industry strength, NASA scientists have also examined the particle radiation in the location with the Solar, Anomalous, and Magnetospheric Particle Explorer, or SAMPEX—the first of NASA’s Smaller Explorer missions, released in 1992 and offering observations right until 2012. A single study, led by NASA heliophysicist Ashley Greeley as portion of her doctoral thesis, applied two many years of data from SAMPEX to exhibit that the SAA is slowly but surely but steadily drifting in a northwesterly direction. The benefits helped confirm products made from geomagnetic measurements and confirmed how the SAA’s spot alterations as the geomagnetic industry evolves.
“These particles are intimately affiliated with the magnetic field, which guides their motions,” reported Shri Kanekal, a researcher in the Heliospheric Physics Laboratory at NASA Goddard. “Thus, any knowledge of particles offers you facts on the geomagnetic field as properly.”
Greeley’s outcomes, revealed in the journal Place Weather, had been also able to deliver a distinct photo of the type and amount of particle radiation satellites get when passing as a result of the SAA, which emphasized the require for continuing checking in the region.
The facts Greeley and her collaborators garnered from SAMPEX’s in-situ measurements has also been helpful for satellite layout. Engineers for the Very low-Earth Orbit, or LEO, satellite utilised the effects to design and style devices that would avoid a latch-up celebration from leading to failure or loss of the spacecraft.
Modeling a safer foreseeable future for satellites
In buy to understand how the SAA is altering and to prepare for upcoming threats to satellites and devices, Sabaka, Kuang and their colleagues use observations and physics to lead to global types of Earth’s magnetic area.
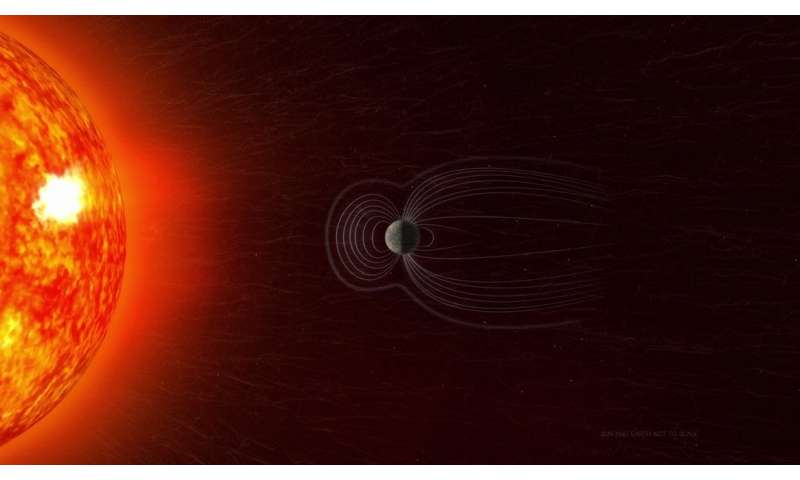
The group assesses the present point out of the magnetic area making use of information from the European Place Agency’s Swarm constellation, prior missions from businesses about the environment, and floor measurements. Sabaka’s crew teases apart the observational details to individual out its source before passing it on to Kuang’s staff. They incorporate the sorted facts from Sabaka’s team with their main dynamics model to forecast geomagnetic secular variation (fast improvements in the magnetic industry) into the potential.
The geodynamo products are one of a kind in their capability to use main physics to develop in the vicinity of-long term forecasts, claimed Andrew Tangborn, a mathematician in Goddard’s Planetary Geodynamics Laboratory.
“This is very similar to how weather conditions forecasts are produced, but we are working with significantly for a longer period time scales,” he reported. “This is the essential variation between what we do at Goddard and most other investigate groups modeling adjustments in Earth’s magnetic discipline.”
Just one these types of application that Sabaka and Kuang have contributed to is the Global Geomagnetic Reference Industry, or IGRF. Applied for a assortment of research from the core to the boundaries of the atmosphere, the IGRF is a assortment of applicant styles designed by all over the world investigation teams that describe Earth’s magnetic subject and track how it modifications in time.
“Even nevertheless the SAA is slow-transferring, it is heading via some adjust in morphology, so it can be also critical that we continue to keep observing it by obtaining ongoing missions,” Sabaka explained. “Due to the fact that is what assists us make types and predictions.”
The altering SAA provides researchers new chances to realize Earth’s main, and how its dynamics affect other elements of the Earth program, said Kuang. By monitoring this little by little evolving “dent” in the magnetic field, researchers can improved fully grasp the way our world is changing and aid get ready for a safer upcoming for satellites.
Analyze reveals unusual magnetic behaviour 8-11 million decades back
NASA’s Goddard House Flight Centre
Citation:
NASA researchers keep track of bit by bit splitting ‘dent’ in Earth’s magnetic industry (2020, August 17)
retrieved 17 August 2020
from https://phys.org/news/2020-08-nasa-monitor-little by little-dent-earth.html
This document is topic to copyright. Aside from any good dealing for the purpose of personal research or study, no
part may well be reproduced without the need of the composed permission. The articles is provided for details reasons only.

Analyst. Amateur problem solver. Wannabe internet expert. Coffee geek. Tv guru. Award-winning communicator. Food nerd.