NASA/JPL
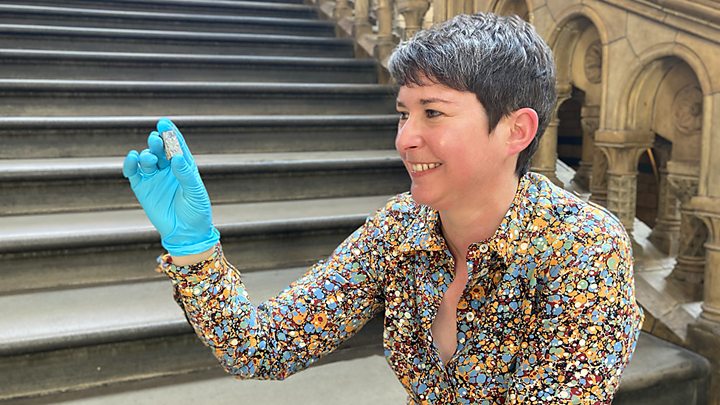
A portion of the Sayh al Uhaymir 008 meteorite which was found in Oman in 1999
A tiny chunk of Mars will be heading property when the US place company launches its hottest rover mission on Thursday.
Nasa’s Perseverance robot will have with it a meteorite that originated on the Crimson World and which, until now, has been lodged in the collection of London’s Purely natural Historical past Museum (NHM).
The rock’s identified houses will act as a calibration concentrate on to benchmark the workings of a rover instrument.
It will give additional self confidence to any discoveries the robotic may well make.
This will be especially crucial if Perseverance stumbles throughout something that hints at the presence of earlier existence on the planet – just one of the mission’s wonderful quests.
“This tiny rock’s got quite a everyday living tale,” stated Prof Caroline Smith, head of Earth sciences collections at the NHM and a member of the Perseverance science crew.
“It shaped about 450 million yrs back, got blasted off Mars by an asteroid or comet approximately 600,000-700,000 decades in the past, and then landed on Earth we don’t know precisely when but most likely 1,000 a long time ago. And now it is going back again to Mars,” she advised BBC News.

Media playback is unsupported on your machine
Learned in the deserts of Oman in 1999, the meteorite, recognised as Sayh al Uhaymir 008, or SaU 008, is a vintage piece of basalt – quite related to the style of igneous rock you will obtain, for example, at Giant’s Causeway in Northern Ireland.
It incorporates lots of pyroxene, olivine and feldspar minerals. And it can be this well-examined chemistry, collectively with the meteorite’s textures, that make it so useful for Perseverance.
The rock has been put in a housing, alongside with nine other varieties of product, on the entrance of the rover in which it will be scanned from time to time by the Sherloc instrument.
This is a software that incorporates two imagers and two laser spectroscopes, which collectively will look into the geology of the rover’s landing website – a 40km-wide crater referred to as Jezero.
Satellite pictures suggest the bowl after held a lake, and experts consider it to be just one of the most effective sites on Mars to check out to come across proof of earlier microbial exercise – if at any time that took position.
Impression copyright
PA Media
Giant’s causeway: The Entire world Heritage internet site is produced from columns of basalt rock
Sherloc will review the nearby rocks and soil, on the lookout for signatures of historic biology.
What researchers you should not want, on the other hand, is to have what they imagine is a “eureka instant” only to then realise Sherloc had formulated some systematic mistake in its observations.
“We’ll glimpse at the calibration concentrate on in the to start with 60-90 times and maybe not yet again for six months mainly because we feel the instrument is really really secure,” reported Dr Luther Beegle, Sherloc’s principal investigator from Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
“But if we start seeing appealing issues on the surface of Mars that we are unable to explain in the spectra, then we’ll glance back to the calibration focus on to make guaranteed that the instrument’s operating the right way.
“I believe the finest we are heading to be ready to do from a scientific standpoint is identify what we would get in touch with a ‘potential bio-signature’.
“I don’t consider we will at any time be essentially 100% absolutely sure for the reason that which is a tricky measurement to make, which is why the sample-return element of Perseverance is so crucial.”
Graphic copyright
NASA-JPL
Artwork: The Sherloc instrument is in the turret on the conclude of the robotic arm
The rover will package its most fascinating rock samples into smaller tubes that will be left on the area of Mars for retrieval and return to Earth by later on missions.
Prof Smith is hopeful she’ll get to function on this product, which could arrive back again in the upcoming 10-15 yrs.
The NHM skilled is on an intercontinental panel that will ascertain how finest to handle the further-terrestrial rocks.
“I am in fact primary the curation emphasis group,” she told BBC News. “By this time future calendar year, we must have a truly good program for the sort of building we will require, the sorts of procedures that will be occurring in that developing, and how we’ll actually commence curating the samples and making them readily available to experts for study.”
Scientists will have a substantially greater chance of confirming lifestyle on Mars if they can evaluate the evidence utilizing all the analytical resources available in Earth laboratories, as opposed to just the tiny suite of devices carried by a robot rover.
Nasa’s Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off on a United Launch Alliance Atlas rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida, for the duration of a two-hour window that commences at 07:50 nearby time (11:50 GMT 12:50 BST).
The slice of SaU 008 will not likely be the only Martian meteorite on board. The rover’s SuperCam instrument will have its possess piece of Mars rock, again to act as a calibration target.
Image copyright
NASA-JSC
The meteorite is a person of 10 calibration targets to be utilized by Sherloc. Others include things like materials that could be utilized in the spacesuits worn by long run human explorers of Mars
Jonathan.Amos-World wide [email protected] isles and adhere to me on Twitter: @BBCAmos

Analyst. Amateur problem solver. Wannabe internet expert. Coffee geek. Tv guru. Award-winning communicator. Food nerd.